Calcium plays a crucial role in ensuring the healthy development of children’s bones and overall well-being. As a vital nutrient, it supports not only bone growth but also the strength and density essential for a child’s physical development. With varied daily calcium requirements based on different age groups, it becomes important for parents to understand and meet these needs through proper diet. Exploring a range of dietary sources and the role of vitamin D in calcium absorption, this article will illuminate the potential consequences of low intake and assess the necessity of supplements, equipping parents with practical strategies to encourage adequate consumption.
Key Takeaways
- Calcium is essential for developing strong and dense bones in children, supporting their overall growth and health.
- Different age groups have specific daily calcium requirements, emphasizing the need for tailored nutritional plans.
- Including a variety of calcium-rich foods like dairy, leafy greens, and fortified products is crucial in a child’s diet.
- Vitamin D plays a vital role in the body’s absorption of calcium, highlighting the importance of a balanced diet.
- Low calcium intake in children can lead to serious health issues, underscoring the importance of adequate consumption.
The Role of Calcium in Bone Growth

Calcium is an essential mineral central to bone development and maintenance in children. From infancy through adolescence, bones are in a constant state of growth and change, necessitating a robust supply of calcium to ensure they grow healthy and strong. Calcium contributes significantly to bone density, which is pivotal in forming a resilient skeletal structure capable of supporting the body’s functions and physical activities.
During this critical growth period, the process of bone mineralization intensifies. Calcium aids in the development of the bone matrix, a framework on which minerals are deposited to strengthen bone tissue. A well-mineralized bone matrix is integral to achieving a peak bone mass during childhood and adolescence, which can help reduce the risk of fractures and osteoporosis later in life.
In growing children, calcium constitutes about 99% of the bone’s content, stored primarily in the form of calcium phosphate, a vital component that lends bones their rigidity. The body’s bone cells constantly remodel this mineral store, absorbing calcium as needed to replace older bone tissue and repair any minor fractures.
Calcium’s role extends beyond mere bone strengthening. It also facilitates other physiological functions such as muscle contraction and nerve transmission, underscoring its systemic importance. Adequate calcium intake during childhood, therefore, not only fortifies bones but also supports overall health and development, laying a solid foundation for a healthier adulthood. Encouraging children to consume calcium-rich foods ensures they receive the necessary amounts to sustain these vital processes.
Daily Calcium Requirements for Different Age Groups
To ensure optimal bone growth and health in children, understanding the daily calcium requirements for different age groups is crucial. The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for calcium varies as children grow:
-
Infants (0-12 months): During the first year, infants typically meet their calcium needs through breast milk or formula. The RDA is set at 200 mg per day for 0-6 months and 260 mg per day for 7-12 months.
-
Toddlers (1-3 years): At this critical stage of development, toddlers require 700 mg of calcium daily to support the rapid growth of bones and teeth.
-
Young Children (4-8 years): The RDA increases to 1,000 mg per day, reflecting the continued growth and increased dietary variety typical of these ages.
-
Preteens (9-13 years): As children approach adolescence, calcium needs rise significantly to 1,300 mg per day. This age marks a period of substantial bone mass accumulation, making adequate calcium intake vital.
-
Teenagers (14-18 years): Teen years continue to be a critical time for bone development, with a sustained requirement of 1,300 mg of calcium per day. This period often involves balancing dietary intake with higher activity levels, necessitating careful attention to nutritional habits.
Ensuring children meet these daily calcium requirements not only supports ongoing bone development and strength but also lays a foundation for healthy bones into adulthood. Parents and caregivers should be mindful of these needs and encourage a balanced diet rich in calcium.
Sources of Calcium in the Diet
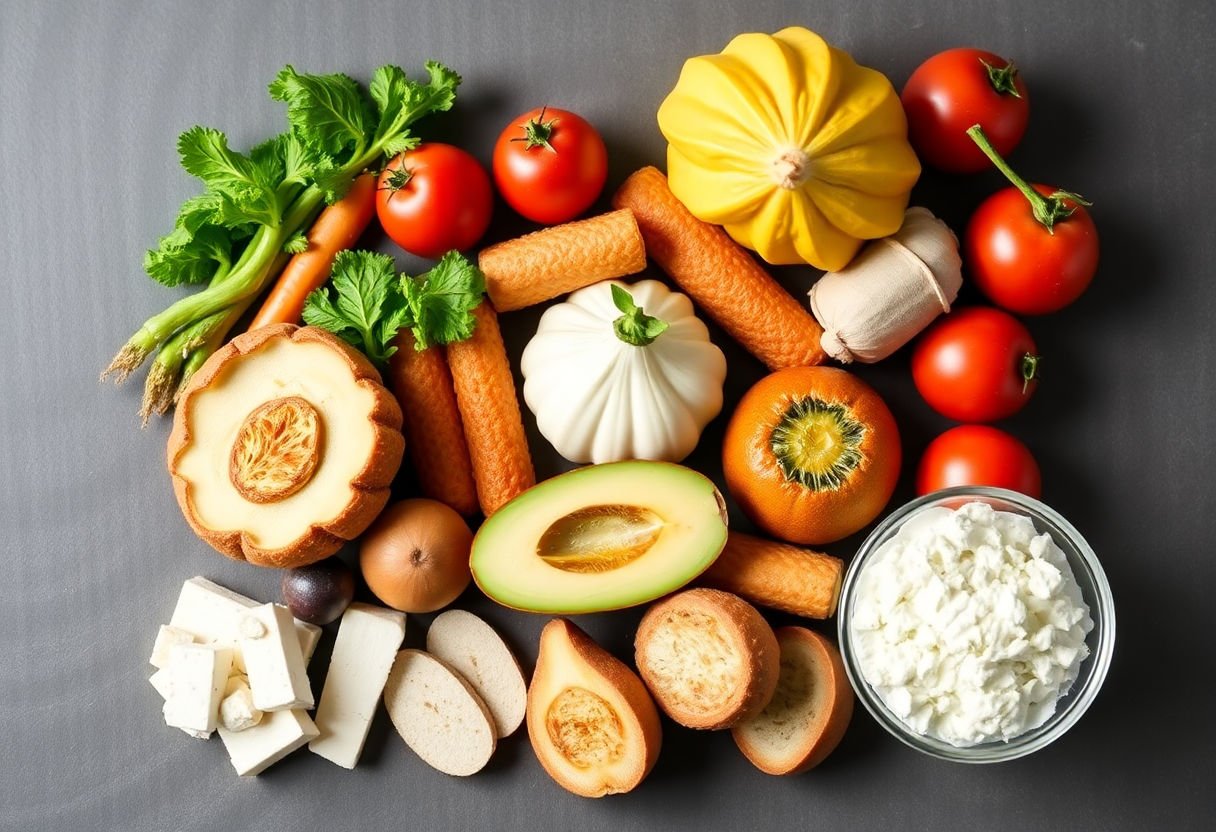

Calcium is an essential nutrient for children, pivotal in their bone development and growth. Ensuring an adequate intake of calcium-rich foods can significantly contribute to building strong and healthy bones. Here are some of the most beneficial dietary sources of calcium:
-
Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt are traditional staples known for their high calcium content. An 8-ounce glass of milk contains about 300 mg of calcium, making it an excellent source for daily consumption.
-
Fortified Foods: Many non-dairy options are fortified with calcium, including plant-based milks (such as almond, soy, and rice milk), orange juice, and cereals. These can be great alternatives for those with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies.
-
Leafy Green Vegetables: Vegetables such as kale, bok choy, and collard greens are not only rich in calcium but also provide a variety of other essential nutrients. Incorporating these into meals can enhance overall dietary value.
-
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, and sesame seeds provide calcium and healthy fats. For example, an ounce of almonds contains approximately 76 mg of calcium.
-
Fish: Canned sardines and salmon with bones are excellent calcium sources. These options benefit not only bone health but also cardiovascular wellness due to their high omega-3 content.
-
Legumes: Beans and lentils, while not as high in calcium as dairy foods, still contribute to daily intake and offer additional fiber and protein beneficial for growing children.
Incorporating a variety of these calcium-rich foods into a child’s diet can help ensure they receive the necessary nutrients for optimal bone health and development.
Calcium Absorption and Vitamin D

Vitamin D plays a crucial role in the effective absorption of calcium, which is essential for building strong bones in children. Without sufficient vitamin D, children’s bodies cannot absorb calcium properly, leading to potential deficiencies that could impede bone development and growth.
When children consume calcium-rich foods, vitamin D is instrumental in facilitating the movement of calcium from the diet into the bloodstream. This occurs primarily in the small intestine, where vitamin D enhances the absorption efficiency of dietary calcium. Foods such as fortified milk and fatty fish can provide both nutrients, maximizing this synergistic effect.
It’s important to note that vitamin D is not produced naturally in the body at adequate levels. Instead, sunlight exposure allows the skin to synthesize vitamin D, which is why moderate sun exposure, combined with dietary intake, is recommended for children to meet their needs. Typically, children require about 15 micrograms (600 IU) of vitamin D daily.
Moreover, during periods of rapid bone growth in children, such as adolescence, the demand for calcium and vitamin D increases significantly. Inadequate levels during these critical years could lead to long-term health issues, including rickets or osteoporosis.
Parents should ensure that their children receive enough vitamin D either through sensible sun exposure, diet, or supplements when necessary. This, in collaboration with a calcium-rich diet, will support optimal bone health and overall development.
The Impact of Low Calcium Intake
A deficiency in calcium intake can have profound implications for a child’s health, potentially leading to a host of developmental issues. Calcium is a vital component in the formation of strong bones and teeth, and insufficient levels can prevent children from reaching their full height potential during their growth years.
Health Complications
When children do not consume enough calcium, they may suffer from impaired bone development, which can result in conditions like osteopenia or even osteoporosis later in life. These conditions are characterized by decreased bone mass and increased fracture risk. In severe cases, a prolonged lack of calcium during the critical growth phases can lead to rickets, a condition marked by soft and weak bones, often resulting in skeletal deformities.
Impediments to Maximal Growth
Children with low calcium intake may experience reduced bone density, which can limit their ability to build peak bone mass. This is crucial because the maximum bone density achieved during youth significantly affects bone health in later life.
Beyond Bones
Low calcium levels are not only detrimental to skeletal health. Calcium also plays a critical role in nerve function, muscle contraction, and blood clotting. Insufficient intake can lead to issues such as muscle cramps and abnormal heart rhythms, affecting a child’s overall wellbeing and daily activities.
Addressing these potential risks by ensuring an adequate calcium intake is essential for the long-term health and development of children. Parents and healthcare providers should work together to assess dietary habits and make adjustments as needed to support healthy growth.
Calcium Supplements: Are They Necessary?
When considering whether calcium supplements are necessary for children, it is essential to evaluate their dietary intake and individual health needs. Primary dietary sources of calcium, such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods, typically provide sufficient calcium for many children. However, some scenarios may warrant additional supplementation.
A pediatrician may recommend calcium supplements if a child has dietary restrictions or allergies that limit their access to calcium-rich foods. For instance, children with lactose intolerance or a vegan diet may struggle to consume adequate calcium through regular meals.
Medical conditions such as malabsorption disorders or certain medications can also impact calcium absorption and may necessitate supplements. Furthermore, during rapid growth phases or increased physical activity, a child’s calcium requirements might increase, making it more challenging to meet these needs through diet alone.
Before administering supplements, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and to avoid excessive calcium intake, which can lead to potential side effects such as kidney stones or impaired absorption of other vital minerals.
In essence, while the majority of children receive adequate calcium from a balanced diet, supplements can be a practical solution in specific cases where dietary intake falls short. Making informed decisions regarding supplements is vital to ensure the optimal health and development of growing kids.
Encouraging Kids to Consume Calcium
To encourage children to consume more calcium, it’s essential to make the process enjoyable and seamless. Ensuring children receive adequate calcium is vital for developing strong bones and maintaining optimal health.
One effective strategy is to incorporate a variety of calcium-rich foods into their daily diet. Offering a wide selection such as milk, yogurt, cheese, fortified cereals, and leafy green vegetables can make meals more appealing and introduce beneficial nutrients.
Creative meal presentations can significantly increase children’s interest in calcium-rich foods. For example, using cookie cutters to shape cheese slices or arranging fruits and vegetables into fun designs on a plate can make snacks more engaging.
Mixing calcium-rich foods into favorite dishes is another subtle method. Adding shredded cheese to scrambled eggs, spinach to smoothies, or blending yogurt into pancake batter can boost calcium intake without compromising on taste.
Education is a powerful tool in promoting healthy eating habits. Teaching children about the importance of calcium for bone growth through fun facts or storytelling can pique their curiosity. An informed child is more likely to make thoughtful food choices.
Moreover, involving children in the kitchen during meal preparation encourages them to try new foods. Allowing them to help prepare meals exposes them to different ingredients and can increase their willingness to taste new dishes.
Ultimately, fostering a positive eating environment where children feel encouraged to explore and enjoy a variety of foods is key to increasing their calcium intake effortlessly. By integrating these practices, parents can help ensure that their children receive the calcium they need for strong, healthy bones.
Conclusion
Ensuring adequate calcium intake is imperative for the healthy development of children, as it lays the foundation for strong bones and overall well-being. The article highlights how meeting the recommended daily calcium requirements through a balanced diet can prevent potential health issues caused by low calcium levels. In the future, emphasizing the interrelationship between calcium and vitamin D will be crucial for maximizing absorption. Parents are encouraged to integrate calcium-rich foods into their children’s diets, while considering supplements when necessary, to support their growth and lifelong health. With informed choices, we can nurture a healthier, robust future generation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the importance of calcium in a child’s diet?
Calcium is crucial for the development and maintenance of strong bones and teeth in children. It also plays a key role in muscle function, nerve signaling, and hormone release, all of which are essential for overall growth and health.
How can I ensure my child gets enough calcium if they are lactose intolerant?
Parents can provide calcium through lactose-free dairy products, calcium-fortified plant-based milks, leafy green vegetables, and nuts. Ensuring a balanced diet with a variety of calcium-rich foods is essential.
Is it safe to give children calcium supplements?
Calcium supplements may be necessary if dietary intake is insufficient, but it is important to consult a healthcare provider to avoid excessive intake. Over-supplementation can lead to health issues such as constipation and impaired absorption of other minerals.
How does vitamin D influence calcium absorption in children?
Vitamin D enhances the body’s ability to absorb calcium, which is vital for bone health. Children can obtain vitamin D through exposure to sunlight, fortified foods, and supplements if recommended by a healthcare professional.
What are the signs of calcium deficiency in children?
Signs of calcium deficiency can include frequent muscle cramps, brittle nails, and dental problems. In severe cases, delayed growth and development could occur, emphasizing the need for adequate calcium intake in growing children.


